On February 11, 2014, Mark Hulbert of MarketWatch.com posted an article titled “Scary 1929 Market Chart Gains Traction (found here)”. In the article, Hulbert suggests that the critics of the chart, which shows a parallel between the current market action since July 2012 and 1928-1929, are running out of explanations as to why the chart doesn’t have merit.
One aspect missing from the Hulbert article is what it takes to get from the most recent high of 16,588 to the 1,658 level on the Dow Jones Industrial Average. In order to lose -89% in value, the Dow would need to decline first to 15k, 14k, 13k etc. Leaving out these important hurdles on the downside ignores a wide swath of goings-on that needs to occur in between now and the doomsday low. To fill the void that is unexamined by the Hulbert article, we’re going to review the various ways that the Dow Jones Industrial Average could decline to new lows.
Before offering our downside take on the market, we’d like to refer you to some basic issues that are mandatory to understanding how the stock market decline from 1929 was an anomaly, at best. In previous work on the topic, we’ve addressed reasons why the 1929 stock market decline of -89% had more to do with reshuffling of the index by replacing stocks that had fallen significantly with new stocks that had appeared strong but were on the cusp of major declines. Once the new stocks were added to the index they crashed hard while the stocks that were dropped from the index were at the beginning stages of recovery (2009 article found here).
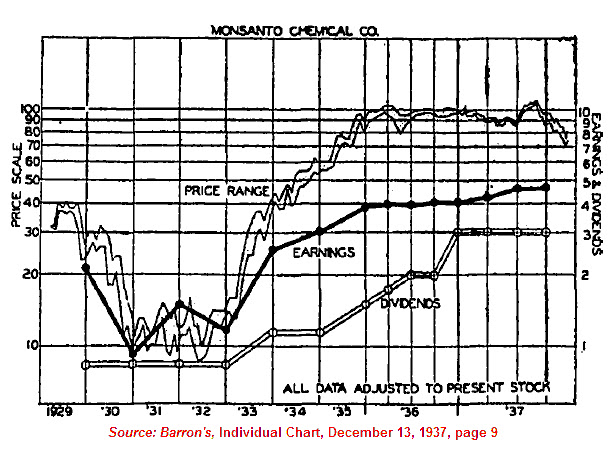
In another piece, we outlined the fact that the decline of 1929 was followed by a recovery that was much faster than most investors know. Our theory is that the multiple changes to the index artificially suppress the index on the way down and on the way up. This resulted in the Dow taking 25 years to achieve breakeven status with 1929. However, stocks that were not part of the index can be seen to achieve breakeven status on average by 1937. One of our favorite examples is found in the chart of Monsanto Corp. below (2010 article found here).